在 自定义View(1)-测量中已经讲过 onMeasure, 而onLayout的内容也不多. 因此下面结合二者, 通过几个实际案例说明它们的作用.
onLayout
onLayout 是 ViewGroup中的一个抽象方法, 因此所有的自定义ViewGroup都需要实现它
protected abstract void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b);
案例–流式布局(FlowLayout)
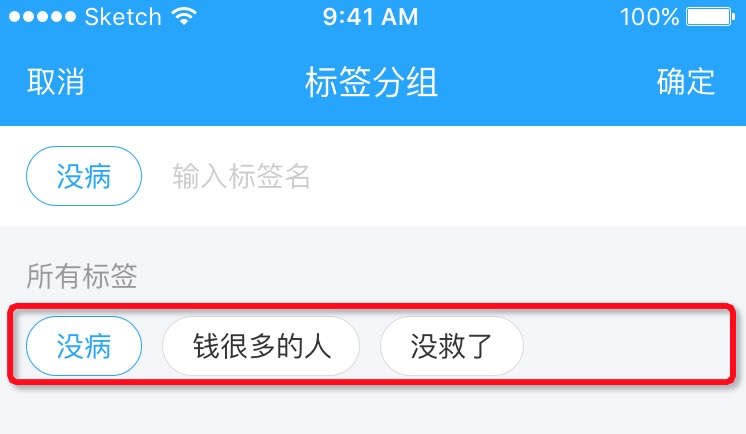
要求如上, 假设现在要用一个容器来存放一组标签, 标签的数量, 长度都不定, 要求是从左向右摆放, 一行放不下就换行. 显然这个功能需要通过一个自定义ViewGroup来实现.
添加必要的自定义属性
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<declare-styleable name="FlowLayout">
<!-- 水平间距 -->
<attr name="columnSpace" format="dimension" />
<!-- 垂直间距 -->
<attr name="rowSpace" format="dimension" />
<!-- 最大行数 -->
<attr name="maxLines" format="integer" />
</declare-styleable>
</resources>
FlowLayout
public class FlowLayout extends ViewGroup {
protected int columnSpace, rowSpace, maxLines;
public FlowLayout(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public FlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public FlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
// 读取自定义属性
TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.FlowLayout);
columnSpace = a.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.FlowLayout_columnSpace, dip2px(10));
rowSpace = a.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.FlowLayout_rowSpace, dip2px(5));
maxLines = a.getInt(R.styleable.FlowLayout_maxLines, 0);
a.recycle();
}
public int dip2px(float dpValue) {
final float scale = getContext().getResources().getDisplayMetrics().density;
return (int) (dpValue * scale + 0.5f);
}
// 测量
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
int pl = getPaddingLeft();
int pt = getPaddingTop();
int pr = getPaddingRight();
int pb = getPaddingBottom();
int lines = 1,
int lineHeight = 0;
int left = pl;
int top = pt;
// 获得容器宽度
int width = resolveSize(getMeasuredWidth(), widthMeasureSpec);
int childCount = getChildCount();
View child;
int childWidth;
int childHeight;
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
child = getChildAt(i);
// 测量子View
measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
// 计算行高
lineHeight = Math.max(childHeight, lineHeight);
// 如果当前行剩余宽度不够用了, 就换行
if (left + childWidth > width - pr) {
// 如果设置了最大行数, 则控制不要超过 maxLines
if (maxLines > 0 && ++lines > maxLines) {
break;
}
// 重置 left
left = pl;
// top 加上 行高 和 行间距
top += lineHeight + rowSpace;
lineHeight = childHeight;
}
// 没算完一个子View, left 加上 childWidth 和 列间距
left += childWidth + columnSpace;
}
// 计算自己的宽高, 并通过 setMeasuredDimension 保存
if (childCount == 0) {
setMeasuredDimension(width, 0);
} else {
setMeasuredDimension(width, resolveSize(top + lineHeight + pb, heightMeasureSpec));
}
}
// 布局
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
int pl = getPaddingLeft();
int pr = getPaddingRight();
int lines = 1;
int lineHeight = 0;
int left = pl;
int top = getPaddingTop();
int width = r - l;
View child;
int childWidth;
int childHeight
for (int i = 0, end = getChildCount(); i < end; i++) {
child = getChildAt(i);
childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
lineHeight = Math.max(childHeight, lineHeight);
if (left + childWidth > width - pr) {
if (maxLines > 0 && ++lines > maxLines) {
break;
}
left = pl;
top += lineHeight + rowSpace;
lineHeight = childHeight;
}
// 对子View进行布局
child.layout(left, top, left + childWidth, top + childHeight);
left += childWidth + columnSpace;
}
}
// 保存状态
@Override
protected void onRestoreInstanceState(Parcelable state) {
FlowState ss = (FlowState) state;
super.onRestoreInstanceState(ss.getSuperState());
columnSpace = ss.columnSpace;
rowSpace = ss.rowSpace;
maxLines = ss.maxLines;
}
// 恢复状态
@Override
protected Parcelable onSaveInstanceState() {
FlowState state = new FlowState(super.onSaveInstanceState());
state.columnSpace = columnSpace;
state.rowSpace = rowSpace;
state.maxLines = maxLines;
return state;
}
public <T> void setData(List<T> list, @NonNull Delegate delegate){
if(list == null || list.isEmpty()){
removeAllViews();
}else {
// 已有几个子view
int childCount = getChildCount();
// 需要几个子view
int size = list.size();
// 复用
if(size > childCount){
// 补充缺少的数量
for (int i = childCount; i < size; i++) {
addView(delegate.initItem(getContext(), i, null));
}
}else if(size < childCount){
// 删除多余的数量
for (int i = childCount - 1; i >= size; i--) {
removeViewAt(i);
}
}
int max = Math.min(childCount, size);
for (int i = 0; i < max; i++) {
delegate.initItem(getContext(), i, getChildAt(i));
}
}
}
public interface Delegate{
View initItem(Context context, int index, @Nullable View view);
}
private static class FlowState extends BaseSavedState {
public static final Creator<FlowState> CREATOR = new Creator<FlowState>() {
@Override
public FlowState createFromParcel(Parcel source) {
return new FlowState(source);
}
@Override
public FlowState[] newArray(int size) {
return new FlowState[size];
}
};
int columnSpace, rowSpace, maxLines;
FlowState(Parcel source) {
super(source);
columnSpace = source.readInt();
rowSpace = source.readInt();
maxLines = source.readInt();
}
FlowState(Parcelable superState) {
super(superState);
}
@Override
public void writeToParcel(Parcel out, int flags) {
super.writeToParcel(out, flags);
out.writeInt(columnSpace);
out.writeInt(rowSpace);
out.writeInt(maxLines);
}
}
}
案例-网格布局(GridLayout)

*
自定义属性
<resources>
<!-- 自定义空View控件相关属性 -->
<declare-styleable name="GridLayout">
<!-- 水平间距 -->
<attr name="grdColumnSpace" format="dimension" />
<!-- 垂直间距 -->
<attr name="grdRowSpace" format="dimension" />
<!-- 列数 -->
<attr name="grdColumnCount" format="integer" />
<!-- item 高 : 宽 -->
<attr name="grdRadio" format="float"/>
<!-- item 高度 -->
<attr name="grdItemHeight" format="dimension"/>
</declare-styleable>
</resources>
GridLayout(流程都差不多, 不详细注释了)
public class GridLayout extends ViewGroup {
protected int columnSpace, rowSpace, columnCount, itemHeight;
protected float grdRadio;
public GridLayout(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public GridLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public GridLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.GridLayout);
columnSpace = a.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.GridLayout_grdColumnSpace, dip2px(10));
rowSpace = a.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.GridLayout_grdRowSpace, dip2px(5));
columnCount = a.getInt(R.styleable.GridLayout_grdColumnCount, 1);
itemHeight = a.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.GridLayout_grdItemHeight, 0);
grdRadio = a.getFloat(R.styleable.GridLayout_grdRadio, 1F);
a.recycle();
}
public int dip2px(float dpValue) {
final float scale = getContext().getResources().getDisplayMetrics().density;
return (int) (dpValue * scale + 0.5f);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
int childCount = getChildCount();
if (childCount > 0) {
int pl = getPaddingLeft();
int pt = getPaddingTop();
int pr = getPaddingRight();
int pb = getPaddingBottom();
int width = resolveSize(getMeasuredWidth(), widthMeasureSpec);
// 强制设置所有 子View 的宽度
int childWidth = columnCount <= 1 ? width - pl - pr : (width - pl - pr - (columnCount - 1) * columnSpace) / columnCount;
// 设置子View的高度
int childHeight = itemHeight > 0 ? itemHeight : (int) (childWidth * grdRadio);
View child;
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
child = getChildAt(i);
// 既然已经强制设置了宽高, 直接测量即可
child.measure(MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(childWidth, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY), MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(childHeight, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY));
}
int rows = columnCount <= 1 ? childCount : (int) Math.ceil(childCount * 1.0 / columnCount);
setMeasuredDimension(MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(width, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY), MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(pt + pb + rows * childHeight + (rows - 1) * rowSpace, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY));
}
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
int childCount = getChildCount();
if (childCount > 0) {
int pl = getPaddingLeft(), pt = getPaddingTop();
View child;
int childWidth, childHeight, cIndex, rIndex, left, top;
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
cIndex = columnCount <= 1 ? 0 : i % columnCount;
rIndex = columnCount <= 1 ? i : i / columnCount;
child = getChildAt(i);
childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
left = pl + cIndex * (columnSpace + childWidth);
top = pt + rIndex * (rowSpace + childHeight);
child.layout(left, top, left + childWidth, top + childHeight);
}
}
}
}
通过上面两个例子, 可以简单的总结下自定义ViewGroup的常规套路:
- 重写 onMeasure(), 测量子VIew, 最后再根据具体要求计算自己的宽高
- 重写 onLayout(), 根据要求对子View进行布局
如何支持Margin
事实上上面的写法在一般情况下使用都没什么问题. 不过我们在测量和布局的时候, 都忽略子View的一个非常重要的属性 Margin. 如果要考虑Margin的影响, 那么需要完成以下步骤:
- 重写ViewGroup中三个关于LayoutParams的方法
@Override protected LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(LayoutParams p) { return new MarginLayoutParams(p); } @Override public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) { return new MarginLayoutParams(getContext(), attrs); } @Override protected LayoutParams generateDefaultLayoutParams() { return new MarginLayoutParams(LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT); } - 修改测量逻辑
- 改 measureChild() 用 measureChildWithMargins()
- 在测量计算中, 要考虑margin的影响:
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams(); int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin; ...
- 修改布局逻辑(代码略)
完!



